NFT Infrastructure – the Next High Ground to Seize
HashKey Capital Research Scarlett Xiao
*Unauthorized reprinting is prohibited. Please indicate the source for reprinting.

Abstract
The market capitalization and trading volume of NFT have been growing tremendously in 2021. Some highly priced products and the celebrity effect make NFT a hot topic in the community. More and more institutions, celebrities, intellectual properties (IP) and retail investors are entering this emerging field. NFT is at its early stage of development, from building single NFT projects (e.g. games, trading platforms, etc.) to exploring high-usability bottom-layer NFT infrastructure. There are also large projects or IPs which self-develop the blockchain for their own NFT issuance, enhancing the NFT ecosystem. In our opinion, it is difficult for NFT to scale due to the congestion and high gas fee issues of Ethereum. To tackle this, there are mainly three infrastructure solutions –NFT-friendly Layer 1 blockchain other than Ethereum, side chains, and Layer 2 Ethereum scaling solutions. We believe that solutions suitable for NFT’s development include public blockchains such as Flow and Near; side chains such as Polygon, xDai and Ronin; and Layer 2 scaling solution like Immutable X.
- Infrastructure Challenges in the Fast-growing NFT Market
1.1 NFT has drawn increasing attention. As of 26 April 2021, NFT market capitalization almost reached US$26 billion. Its trading volume exceeds US$1.5 billion in Q1 2021, 26x from the previous quarter, and 70% of the volume concentrates on NBA Top Shot, Crypto Punks and Opensea. Meanwhile, NFT pricing has been increasing in 2021 as shown in Figure 1. Beeple’s collaged digital artwork NFT, Everydays: The First 5000 Days, was sold at US$69.35 million. The first Twitter post NFT of Jack Dorsey, Founder of Twitter, was sold at US$2.9 million. Such highly priced products and the celebrity effect make NFT a hot topic in the community. In table 1, we summarize major NFT events in 2021.
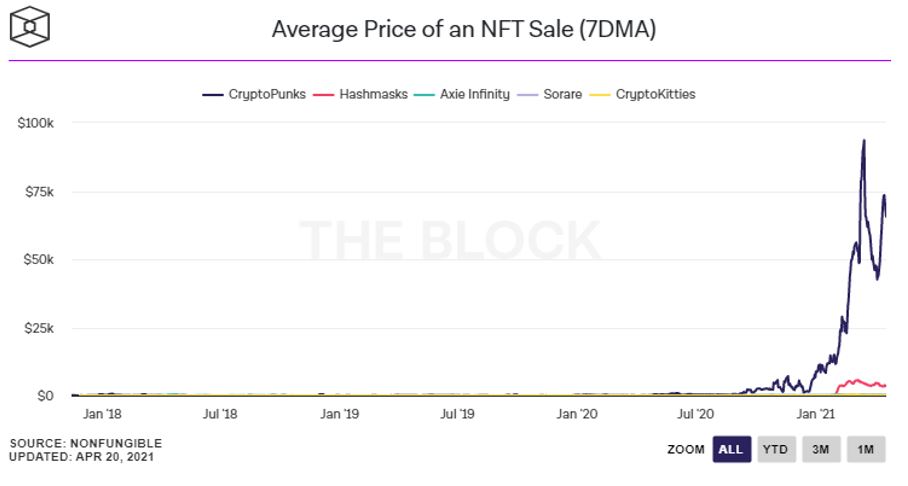
Figure 1. Average Price of an NFT Sale (Source: The Block)
| Time | Event |
| 20 Apr 2021 | Snoop Dogg, a rapper, issues NFT with Nyan Cat |
| 19 Apr 2021 | Paris Hilton, the successor of Hilton Group and celebrity, issues NFT |
| 17 Apr 2021 | NSA whistle blower Edward Snowden sells the first NFT for over US$5 million |
| 14 Apr 2021 | Grammy Winner Ryan Tedder issues NFT on Origin |
| 9 Apr 2021 | Professional wrestling company WWE releases its first-ever NFTs, showcasing iconic moments of legendary The Undertaker |
| 7 Apr 2021 | McDonald’s France announces to create NFT artworks representing certain popular dishes on their menu |
| 7 Apr 2021 | Pak and Sotheby’s team up for their first NFT auction on Nifty Gateway |
| 5 Apr 2021 | Luxury brands like Gucci announce the plan to issue NFT |
| 1 Apr 2021 | Grammy-winning singer The Weeknd announces to launch new songs and limited-edition artworks on Nifty Gateway |
| 29 Mar 2021 | Justin Sun sets up the JUST NFT fund, focusing on NFT artworks |
| 26 Mar 2021 | NFT of New York Times column sells for 50 ETH |
| 21 Mar 2021 | Twitter CEO Jack Dorsey sells the first tweet for US$2.9 million |
| 18 Mar 2021 | American professional skateboarder Tony Hawk teams up with Ethernity to issue NFT |
| 11 Mar 2021 | Digital artist Beeple’s NFT artwork “Everydays: The First 5000 Days” sells for US$69.35 million |
| 2 Mar 2021 | Grimes, Elon Musk’s partner, sells a digital artwork for US$5.8 million on Nifty Gateway |
| 17 Feb 2021 | British auction house Christie’s holds the first blockchain-based NFT art auction |
| 8 Feb 2021 | Linkin Park Singer Mike Shinoda sells NFT on Zora |
Table 1. Major NFT Events in 2021
1.2 The scale of NFT is restricted by high cost and low capacity of Ethereum. As of 26 April 2021, 8 out of the top 10 NFT projects by sales are built on Ethereum, including CryptoPunks, Hashmasks, CryptoKitties, Sorare, Axie Infinity, Art Blocks, MyCryptoHeros and Gods Unchained. Meanwhile, as shown in Figure 2, the average Ethereum transaction fee has increased significantly in 2021 to US$20 per transaction in Feb and US$18 in March. Although the gas fee reduced in April, it is still not friendly to high frequency trading. Ethereum’s low-capacity results in the following issues in the NFT field.
- High cost of tokenization. NFT tokenization is more complex compared to other processes such as trading. The gas fee for tokenization is very high. For example, in February or March, the gas fee can be as high as US$200 to tokenize one painting. In April, it was still at around US$100. In many cases, the tokenization fee is more than the NFT price itself.
- High cost and low speed of trading. Most Ethereum-based NFT trading platforms need to pay gas fees to buy and sell tokens (except that Nifty Gateway allows users to pay with credit cards), and even to pull the artwork off the shelf. For example, Mintable trading platform charges 2.5% of the bidding price as the transaction fee. In addition, the platforms are slow in transferring fund, taking 3-5 minutes to confirm one transaction.
- Bad user experience. The speed of moving of player’s roles in the game is much slower than a Web-based game, with significant delay. In some games, users have to pay gas fees every time they make a move, resulting in unsatisfying user experience and creating difficulties in customer retention and acquisition.
The major issues of the Ethereum network are high transaction fee, network congestion, and unsatisfying user experience. It makes the adoption of NFT, a high-barrier-of-entry product, even more difficult. Many retailer investors do not enter this market because of the high transaction fee. In addition, Ethereum can not achieve cross-chain operation. Hence, it is critical for the NFT industry to look for a scalable solution that supports high frequency trading.
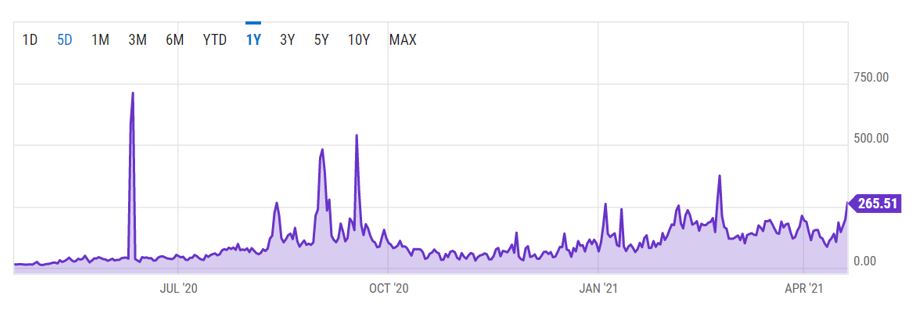
Figure 2. Historical Ethereum Gas Fee (Source: Ychart)
Public blockchain, side chains and Layer 2 solutions are three alternatives
Although Ethereum is strong in Defi, its advantages on Web 3.0 and NFT areas such as gaming, social media, and communications have not been seen. That provides new market opportunities for emerging public blockchain, side chains and Layer 2 solutions. In general, we do not believe that there will be any absolute winner in NFT infrastructure. However, solutions with highly competitive technology and high-quality ecosystem could better drive product adoption in the market, more likely to become leading projects of NFT infrastructure.
- Public Blockchain
2.1 Flow
2.1.1 Development by Dapper Labs, creator of Crypto Kitties
Flow is a new Layer 1 blockchain, developed by Dapper Labs, creator of Crypto Kitties. Its CTO invented the ERC721 standard which is widely applied in NFT. Dapper Labs has a team of game developers and has built a series of developer platforms before its entry into the blockchain field. After creating Crypto Kitties, the team has been focusing on NFT to solve issues such as capacity and fiat currency deposit and withdrawal, and the Flow public blockchain was then developed. Many team members came from traditional venture investment and sports industry with rich resources. In addition, its view on NFT and the market also drive the integration of capital and market adoption, which is to ensure usability for the right audience. The latest valuation of Dapper Labs has reached US$7.5 billion. Existing products built on Flow include NBA Top Shot, UFC on Flow, NFT trading platform VIV3, browser Flowscan, collection game Dr. Seuss, etc.
2.1.2 Low inflation tokens with multiple use cases
Token FLOW is the native token of the Flow blockchain. FLOW holders can use the token to pay for gas fee, to participate in community governance, to store margin deposit data, as medium of exchange and as the collateral. The total amount of FLOW will not exceed the limit of 1.25 billion, avoiding inflation due to additional issuance and dilution of token holder’s interest. With increasing application and thus gas fee in the future, FLOW’s inflation rate will decrease. When the network fee is lower than the fixed reward for nodes, there will be additional token issuance. Tokens exceeding the rewards for nodes will be kept in a custodian account, to hedge the future token inflation.
2.1.3 Technical advantage: multi-role nodes to achieve scale
Flow’s capacity expansion is achieved by separating the computing and consensus work among nodes in a pipelined architecture, which means that one single node does not participate in the whole transaction computing and verification process, but only in one of the four processes of collection, consensus, execution and verification. Adopting the PoS mechanism, every Flow node needs to stake some tokens, the amount of which determines the size of rewards. Figure 3 illustrates Flow’s working process. Collection nodes summarize and send information to consensus nodes, which confirm the transaction and pass it for execution. Execution nodes then send the computing result to verification nodes for verification. Nodes with a large quantity but low computing capacity can only participate in the verification process. In particular, Samsung participates in execution; DCG is involved in collection, consensus and verification; and CoinFund participates in the consensus process. Such information is all available on Flowscan.org.
![]()
Figure 3. Flow’s Node Operating Process
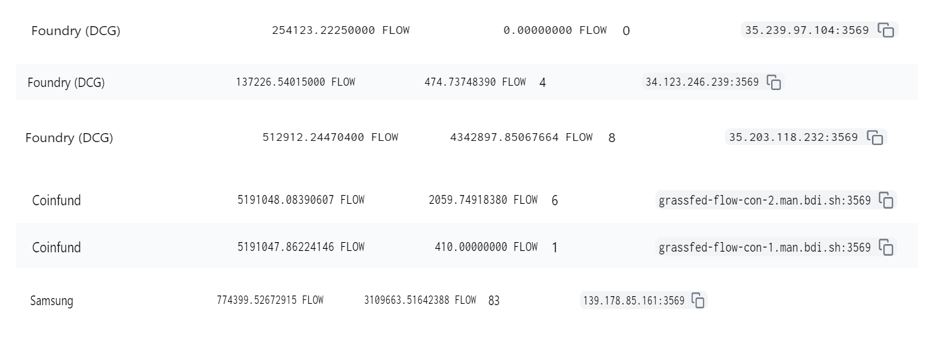
Figure 4. Node Roles of Flow Community Members (Source:Flowscan.org)
In addition, Flow does not divide the network to achieve scale. Developers do not need to worry that shard’s ACDI properties cannot be guaranteed. On-chain smart contracts are in the same shared environment, enabling smoother information exchange between smart contracts. Meanwhile, the workload of nodes reduces so the network does not require highly specialized professional nodes to handle a large number of transactions and thus does not compromise decentralization. The division of work among Flow nodes helps to improve the transaction speed and volume on the entire network, lower the transaction cost and enhance the user experience of developers and consumers.
2.1.4 Market advantages: Strong IP
The main reason that Flow can become the star public blockchain for NFT is its access to quality resources in the ecosystem. The sales of the popular game NBA Top Shot is approaching US$500 million now and we do not explain how popular it is again here. It is supported by the strong NBA IP. Apart from NBA, Flow’s major partners include UFC, Warner Music, famous game developer Animoca, Unisoft, Samsung, NFT trading platform Opeansea, etc. Top sports alliances such as NBA, UFC and NFL attract significant capital and own a fan base of hundreds of millions globally. Personal Twitter of Lebron James has about 50 million followers. Such top IPs provide Flow a significant advantage in the potential client base compared to other public blockchain. Figure 5 lists out community members and partners of the Flow ecosystem. Flow also plans to form a committee of IP holders, entertainment KOLs, and famous gaming companies, to uncover the global entertainment development trend. Flow will be able to secure more entertainment data and resources, and leverage IPs to develop the economies of collectibles and fans.

Figure 5. Flow Community (Source: Flow)
2.1.5 Investment from top institutional investors
Figure 6 lists out the investors of Flow, including famous institutional investors such as a16z, Coinbase Ventures, DCG, USV, etc.

Figure 6. Flow Investors (source: onflow.org)
2.2 Near
2.2.1 Leveraging sharding to become an emerging popular NFT public blockchain
Near Protocol is a decentralized Internet platform. It is a new Doomslug blockchain built on sharding and can be scaled unlimitedly. Near’s high-performing EVM processing capacity can be 10x higher than Ethereum’s. It adopts Nightshade’s dynamic sharding approach to minimize the computing size of contract execution. Transactions can be confirmed within 1-2 seconds and less than US$1 gas fee is charged per transaction on average. EVM has been put on the test net and is expected to be launched on the main net in a couple months. At the moment, the team has over 100 full-time contributors from 10 countries. Near’s investors include institutional investors such as a16z, Coinbase Ventures, Metastable and Accomplice and other angel investors.
2.2.2 Technical advantage: sharding and Rainbow Bridge
2.2.2.1 Nightshade sharding technology to scale effectively
- Sharding effectiveness. Different from Ethereum 2.0, Polkadot and Harmony, Near does not adopt the shard chain and beacon chain model (where every shard chain needs to make the folk choice), but relies on one main chain. Each block of the main chain is sharded into multiple chunks, that is, sharding on the block layers. Block creators and verifiers only need to maintain the accuracy and state of the chunks they participate in. Hence, Near’s block creation time is shorter, sharding effectiveness is higher and data completeness is also improved.
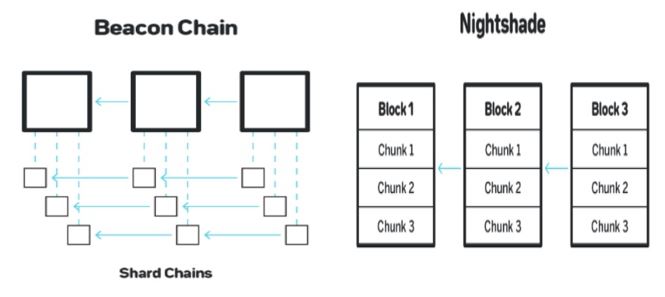
Figure 7. Sharding Model Comparison between Shard Chains and Nightshade
- Shard security. Near randomly distributes validators using the VRF approach where the validator and the corresponding sharding information are not public. Nodes are not aware of the corresponding relationship between the validator and the block. Upon signature, validators only sign on the entire block instead of on the verified chunk, in order to ensure the security of the shard.
- Data reliability. Near’s data reliability and communication solution is that every node separates the created block by itself into multiple pieces and sends them to multiple validators. Validators only need to verify one piece to recover the entire block, achieving data reliability and efficient cross-shard communication.
2.2.2.2 Seamless integration with Ethereum using Rainbow Bridge
The operating principles of Rainbow Bridge are 1) cooperative operation between the Ethereum and Near applications; and 2) the state of the other blockchain can be tracked and read, and relevant operation can be executed without any trusted third party or permission. On-chain assets can be transferred to the other chain via relays after verification. All ERC20 tokens can be freely transferred between Ethereum and Near, allowing the Near ecosystem to be built on top of Ethereum seamlessly. Mature Ethereum infrastructure can be fully leveraged. Users can send ERC20 assets from MetaMask to Near wallets or via Dapps directly, and vice versa, including NFT transfer and using ETH to pay for gas fee.
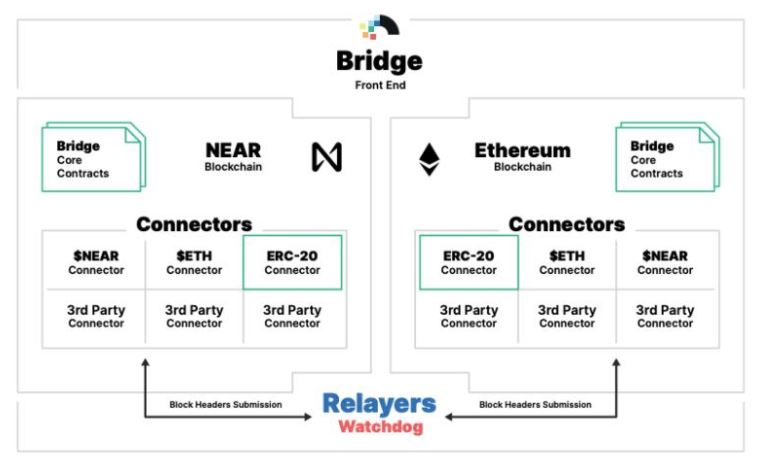
Figure 8. Illustrative Operating Model of Rainbow Bridge (source: Near)
2.2.3 NFT Ecosystem: dominated by NFT trading platforms
Existing NFT projects built on Near are listed as below:
| Trading platform | Mintbase | One-stop NFT shop focusing on niche NFT, including photographs, VR, music, etc. Users need to register a Mintbase store to release products. |
| Paras | A platform for creating, trading and collecting digital art cards (DAC), and a social channel for DAC creators and collectors. | |
| Snark.Art | A digital art trading platform to allow artists to sell NFT assets and manage own communities. | |
| Arterra | A digital collectible trading platform, offerings AR gaming rewards and token rewards to incentivize community participation. | |
| Nearfolio | A NFT marketplace with all on-chain metadata stored on Near blockchain | |
| Game | Berry Club | A Defi game where users can create various NFT with pixels. Liquidity pool rewards are also available. |
Table 2. NFT Projects on Near
There are not many NFT projects built on Near currently. Except Mintbase, others do not have a large user base. Most projects are NFT trading platforms as Near’s sharding technology can well support high frequency trading and batch NFT tokenization. Although there is still a gap between the NFT and Ethereum ecosystem, we expect more NFT projects to use Near in the future with its scalable technology and impact of the feature project Mintbase. Near has the potential to become another popular NFT public blockchain platform.
2.2.4 Feature Project: Mintbase
Mintbase is a one-stop shop built on Near, similar to Taobao for NFT, offering music, painting, artworks, tickets, games and VR. Users can search by stores. Compared to other NFT trading platforms such as Opensea, Mintbase focuses on differentiated niche NFT. Currently, it has over 1,000 stores and over 10,000 registered users, and over 2,000 NFT products have been sold. Mintbase is highly user friendly. Artists, musicians, and normal users without any blockchain knowledge can tokenize their work in a short time, lowering the NFT barrier of entry. On Ethereum, creating a ticket using Mintbase will cost US$60-100. Hence, it is almost impossible to do it at a large scale. Also, registering a store also costs over US$100. However, on Near, less than US$0.01 fee is charged to create a ticket, which can be basically ignored. There are also other reasons why Mintbase chooses Near. For example, it can be better integrated with large Defi projects on Near, like Balancer.
- Side Chains
3.1 Polygon (Matic)
3.1.1 Prosperous NFT ecosystem
Polygon, formerly known as Matic Network, was founded by three Indian crypto community members. It was renamed as Polygon in February 2021 and MATIC is its token. Since then, it adopts popular Zk Rollup and Optimistic Rollup solutions, in addition to the existing Plasma and Matic PoS blockchain. Its direction is still capacity expansion. However, it not only just develops Plasma or side chains, but emphasizes more on the Polygon ecosystem development after renaming Matic.
There has been over 130 Dapps, 270,000 users and 15 million transactions on the main net since it went live in June last year. Most of the Dapps are NFT related, especially gaming ones. As shown in Figure 9, Polygon’s daily active addresses and trading volume have grown tremendously since March 2021. Daily active addresses increased by almost 500% on a quarterly basis and the trading volume also increased by 288%, reaching US$500 million in Q1 2021. However, Polygon Dapps are still at an early stage, except DEX QuickSwap, Defi+NFT game Aavegochi, and horse racing game ZED RUN, most of the other Dapps have less than 100 users. As of now, leading Defi and NFT projects such as lending platform Aave, stablecoin trading protocol Curve and trading platform Opensea choose Polygon as the scaling solutions.
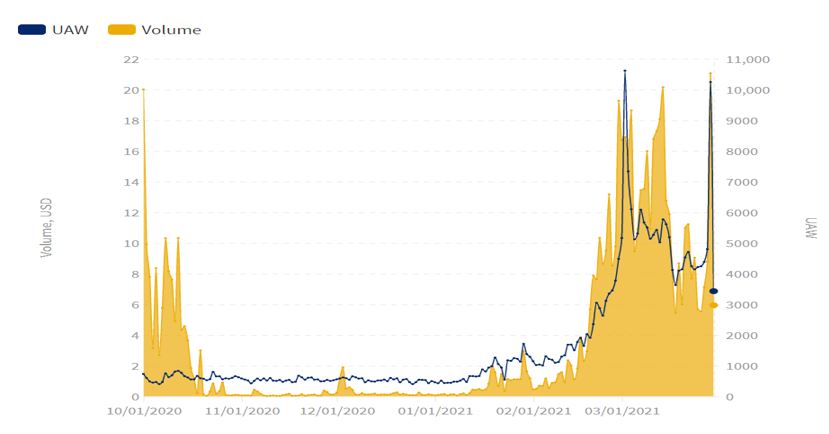
Figure 9. Trading Volume and Daily Active Addresses of Polygon, Q1 2021
(Source: DappRadar)
3.1.2 Technical advantage: multiple scaling solutions
Currently, Polygon leverages Matic Network’s original scaling solutions, including Plasma blockchain and PoS side chain.
- Matic Plasma Chain. Matic Plasma Chain shares the security mechanism with Ethereum, securing the protocol with Proof of Fraud and verification nodes. In the Polygon ecosystem, different protocols can share verification nodes. Although Plasma chain can guarantee security, its asset withdrawal to the Ethereum main chain has a 7-14 day lockup period, less flexible and independent. It is less friendly to small amount and high frequency transactions, but applicable to projects with high security requirements such as Defi contracts with high lockup requirements.
- Matic PoS Chain. Polygon PoS chain is a side chain with its own security and consensus mechanism. It is highly independent and flexible but less secure and exposed to various attacks. Also, such side chains require a large number of verification nodes, applicable to projects with a strong ecosystem or community. For example, the community of a NFT trading platform is large, has high requirements on transaction cost and speed, and is willing to compromise security to some extent. PoS side chains are suitable in this case.
Overall, Polygon combines Plasma and PoS and expands capacity using side chains under the condition of shared security with Ethereum. It enhances efficiency and guarantees security. In addition, Polygon plans to launch SDK to allow developers to use multiple Layer 2 solutions simultaneously. This includes Optimistic Rollup, ZK Rollup, and Validium, which is to turn on the Layer 2 Connector and achieve scale with a mixed solution.
3.1.3 NFT Ecosystem
3.1.3.1 Reasons that Polygon is suitable for NFT application development
We believe that Polygon is suitable for NFT application development for three reasons.
- With Polygon’s technical advantage, gaming Dapp transactions can be processed fast, on average within 1 second per transaction. User experience is similar to that of an off-chain game. Transaction cost is around $US0.00004 per transaction. It solves Ethereum’s high cost and low speed issues, more applicable to NFT games with high frequency trading. In addition, Polygon is compatible with EVM and Metamask.
- Development tool provider, Biconomy, leverages meta-transactions to help users pay gas fee, enhancing Dapp’s user experience.
- In the aspect of art collectibles, NFT tokenization is expensive on Ethereum-based Dapps. Many Dapps cost more than US$100. However, the fee is only 1% of that if it is on Polygon, lowering the barrier of entry for NFT.
3.1.3.2 Dapps dominated by games
Table 3 shows the Polygon’s existing NFT ecosystem. 70% of Dapps are gaming related. Popular ones include leading Defi platform Aave’s ghost collection game Aavegotchi, VR platform Decentral Games, digital horse racing game ZED RUN, space game 0xUniverse, digital collectible platform Showcase, Tweet tokenization platform Tokenized Tweets, gaming developer Animoca’s car racing game F1 Delta Time, leading NFT trading platform Opensea, NFT fractional trading platform Niftex, etc.
Polygon can be seen as the top choice of the settlement layer for most Ethereum-based NFT project’s Layer 2 migration. Polygon has also attracted the participation of some celebrities. For example, Jack Dorsey and Elon Musk sell NFT Tweets on Polygon-enabled platform Cent. Mark Cuban also uses Tokenized Tweets to tokenize his Tweets.

Table 3. NFT Dapps on Polygon (Source: Dapp Radar)
3.1.3.3 Feature Project: Aavegochi
Aavegochi is a Defi+NFT project in the Aave ecosystem. Users can use aToken to pledge ghost Aavegotchi NFT. It is a Defi-supported collectible game. As shown in Figure 10, Aavegotchi’s daily active addresses reached 3,000 in March 2021, making it a popular project in NFT gaming.
Aavegotchi is one of the first Ethereum games migrating to L2. First batch of 10,000 Aavegotchi portals are sold out. Aavegotchi incentivizes the migration of GHST and MATIC token from Ethereum to Polygon with a two-week yield farming campaign. Users can receive token rewards during the migration process. Migrated Aavegotchi token GHST can be fast transferred between Ethereum and Polygon. Also, users can quickly trade gaming properties on Polygon at extremely low costs.
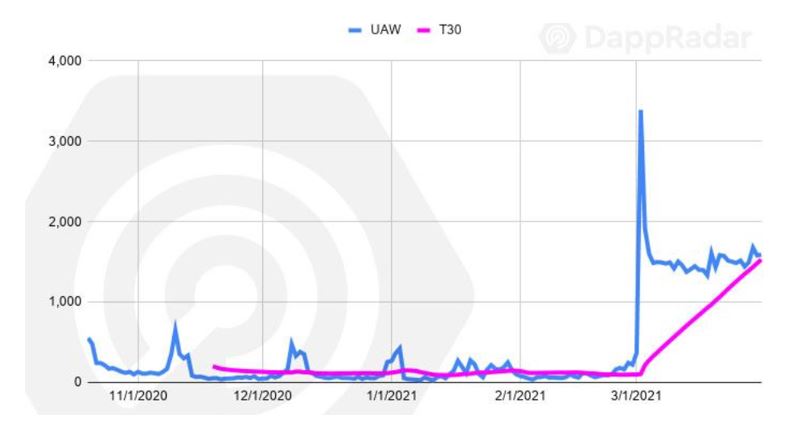
Figure 10. Number of Unique Active Wallets of Aavegochi (source: DappRadar)
3.2 xDai Chain
3.2.1 A side chain launched by MakerDAO
xDai Chain was an Ethereum side chain co-launched by MakerDAO and POA Network, compatible with Ethereum’s EVM. xDAI Chain shares the same parameters with EVM and upgrades together with the Ethereum main net protocol, allowing all Ethereum assets and users to seamlessly migrate to xDai, and vice versa. Key features of xDai side chain include:
- Leverage TokenBridge cross-chain protocol to achieve asset transfer between Ethereum and xDai Chain. When assets are released, multiple signatures are required on the side chain. TokenBridge adopts the PoA mechanism. PoA private key holders have high authority power, indicating the risk of hostile behaviours. However, PoA enhances the cross-chain asset transfer efficiency and provides better user experience.
- On-chain native token xDai is a derivative of the Ethereum stablecoin Dai. They are both pegged to US dollars.
- Adopt a dual-token governance model. In addition to the payment tool xDai, there is also the multi-purpose governance token STAKE on the blockchain. STAKE holders can participate in the network upgrade.
- xDai Chain has its own consensus mechanism – POSDAO. TokenBridge adopts the PoA mechanism. PoA private key holders have high authority power, indicating the risk of hostile behaviours. However, PoA enhances the cross-chain asset transfer efficiency and provides better user experience. From xDai Chain’s blockchain browser, we know that xDai Chain’s validation nodes include famous projects such as POA Network, 1Hive, Gnosis, etc.
- Low cost and fast transaction. Currently users pay US$0.0002 gas fee for each transaction on xDai. Block confirmation speed is around 5 seconds. More and more Dapps choose to migrate to xDai. Some projects only migrate some functions such as voting. Community members are more willing to vote and participate in the community governance when the cost is low.
3.2.2 NFT Ecosystem: dominated by trading platforms
Low cost and high performance make xDai Chain one of the most effective Ethereum extensions. Currently, there are almost 100 Dapps on xDai Chain, covering areas such as ecosystem infrastructure, P2P payment, Defi, DAO governance, data analytics tools, and NFT. Some representative projects include Dune Analytics, Unique One, DeBank, Honeyswap, Perpetual Protocol, Dark Forest, etc. 20% Dapps are NFT projects (19), most of which are trading platforms. Table 4 lists NFT projects on xDai Chain.
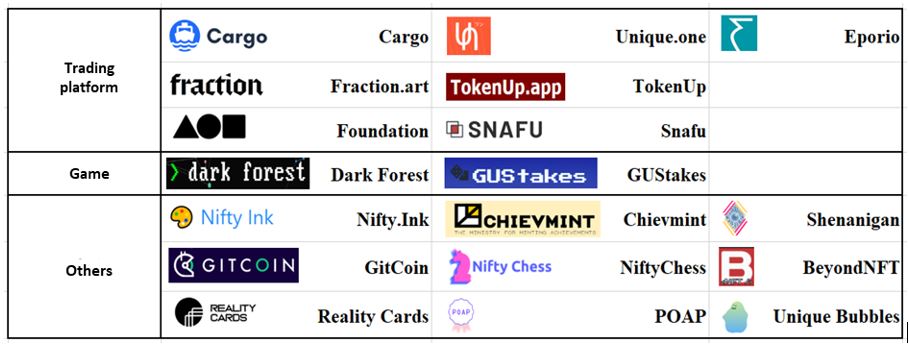
Table 4. NFT Projects on xDai Chain
xDai’s low cost and high performance largely boost the development of NFT applications. Taking NFT tokenization platform Nifty.Ink as an example, tokenization cost can be as high as US$70 on Ethereum. However, tokenization on xDai-based Nifty.Ink costs almost nothing. Also, NFT on xDai can be transferred to Ethereum seamlessly without any cost via TokenBridge, which means NFT from Nifty.Ink can be traded on Opensea.
3.2.3 Feature Project – Dark Forest
The name Dark Forest is from the science fiction The Three-Body Problem. It is a MMO space-conquest game. Players start with randomly located home planets and expand his / her territory by capturing new planets. Dark Forest differs from other conquest games as it leverages zkSNARK to not disclose player’s trajectory. Players can play the game with privacy protection. Specifically, in Dark Forest, players are not aware of other player’s strength level or the distance from their home planets, which makes the game more interesting. Both Vitalik and Matt Huang, co-founder of Paradigm, tweeted to recommend Dark Forest.
Figure 11. Tweets of Vitalik and Matt Huang
In this game, players need to pay gas fee for every move and they normally move multiple times within one minute. This is not achievable on Ethereum because of the delay in move due to the congestion and the significant amount of gas fee. xDai Chain helps to save gas fees and enhance user experience.
Dark Forest has upgraded to v5.0 now from v3.0 in August 2020 and added a special Dark Forest NFT module. When it was upgraded to v4.0 in October 2020, Dark Forest migrated from Ethereum to xDai Chain. Official data shows that Dark Forest contributes 80% of xDai’s transaction volume during those few days, indicating the popularity of Dark Forest. Users do not need to purchase any crypto asset to join the game. The game will offer US$0.05 worth of xDai to every player for gas fee payment and, as an incentive, offer Dai rewards to the top 15 players.
3.3 Ronin
3.3.1 Axie Infinity, a customized side chain
Ronin, built by Axie Infinity’s team Sky Mavis, is a customized Ethereum side chain designed for Axie Infinity. It adopts Proof of Authority (PoA) consensus mechanism, which can be seen as the enhanced version of PoS. To ensure the security and efficiency of the network, the number of validators will not exceed 25 in PoA, less than that in PoS. To some extent, Ronin is a private PoA blockchain serving Sky Mavis and Axie Infinity.
Ronin validators are all trusted partners authorized by Sky Mavis. The test net was live on 23 December 2020 with game developer Unisoft, Animoca and Nonfungible.com as the first validators. Currently, DappRadar and Binance are also Ronin validators. Validators are responsible to create and validate blocks, process the asset transfer and storage between Ronin and Ethereum, including ERC20 tokens and NFT. The main net went live on 1 February 2021 and the first transaction was to transfer the land and properties on the land in Axie Infinity.
3.3.2 Advantages
We believe the advantages of Ronin include:
- Near-real-time fast transactions.
- Extremely low transaction cost.
- Axie can be freely transferred between Ethereum and Ronin.
- Significant enhancement of user experience.
- Customized for Axie Infinity, fitting Axie community’s complicated customization requests.
- Ronin developers focus more on Ronin’s performance as it is built by the same team as Axie Infinity.
Ronin is still at an early stage and its NFT ecosystem is still immature except for Axie Infinity. According to CEO of Sky Mavis, the team will continue to explore effective NFT scaling solutions such as zKSyncs and make Ronin one of the most effective scaling solutions in the NFT gaming field.
3.3.3 Axie Infinity
Axie Infinity is a blockchain strategy game. Players can battle, raise, and trade fantasy creatures called Axies, similar to PokemonGo. The governance token is AXS. Players can earn Small Love Potions (SLP) tokens by breeding new Axies or trade Axies on Opensea.
As of now, the transaction volume of Axie Infinity has almost reached US$20 million and its active user base exceeded 3,000 towards the end of 2020, making Axie Infinity one of the top blockchain games. However, in 2021, as the congestion issue worsens on Ehtereum and gas fee increases, its user base reduces. In January 2021, there were only 523 active users. The development team then planned to launch Ronin to migrate assets.
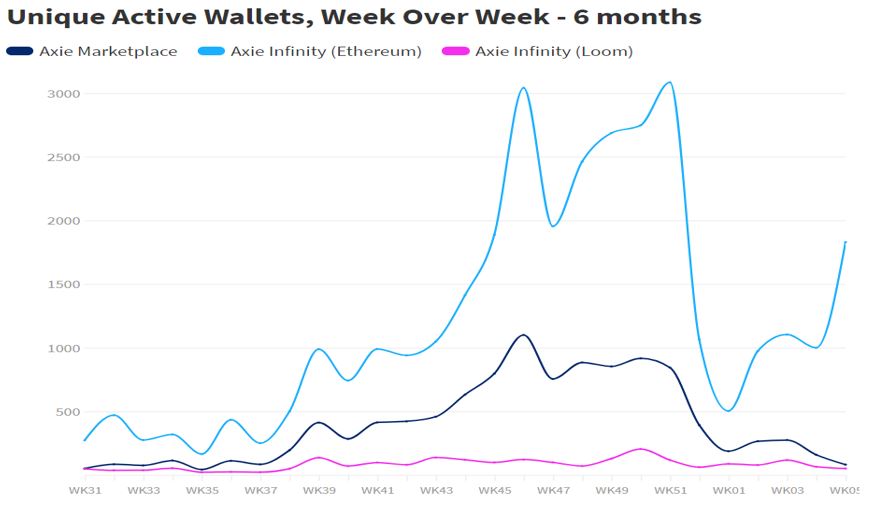
Figure 12. Weekly Unique Active Wallets of Axie Infinity (source: DappRadar)
Axie Infinity’s land and properties on the land were first migrated to Ronin after the main net was launched. Sky Mavis was in charge of the migration but users could also migrate assets by themselves. A new land property in Axie Infinity is offered as a reward for users who completes the migration before March 1. According to the development team, Ronin is now at the first phase of migration, where only ETH can be used to store and migrate land and properties on Ronin and, at the second phase, AXS token will be used for staking on Ronin to upgrade all Axie Infinity smart contracts and all Axie NFT will be migrated to Ronin.
- Layer 2 Scaling Solutions
4.1 Immutable X
4.1.1 Development by the Gods Unchained team
Immutable X, co-launched by the blockchain card game Gods Unchained’s developer Immutable and zero-knowledge proof technology company StarkWare, is a scaling solution designed for Ethereum NFT projects. Australia-headquartered Immutable secured US$15 million investments from Naspers, Galaxy Digital and Apex Capital in 2019. Immutable X adopts the zero-knowledge proof technology and can achieve 9,000 TPS with almost zero gas fee. More and more NFT gaming projects have chosen to use it.
- Layer 2 Scaling Solutions
4.1 Immutable X
4.1.1 Development by the Gods Unchained team
Immutable X, co-launched by the blockchain card game Gods Unchained’s developer Immutable and zero-knowledge proof technology company StarkWare, is a scaling solution designed for Ethereum NFT projects. Australia-headquartered Immutable secured US$15 million investments from Naspers, Galaxy Digital and Apex Capital in 2019. Immutable X adopts the zero-knowledge proof technology and can achieve 9,000 TPS with almost zero gas fee. More and more NFT gaming projects have chosen to use it.
4.1.3 NFT Ecosystem: dominated by games
Currently NFT projects using Immutable X as the L2 scaling solution include card game Gods Unchained, NFT trading platform Mintable, Defi+NFT project SuperfarmDAO, card collection project Epics.GG, battle game Illuvium, game developer Lucid Sight (which owns MLB Champions Baseball, Crypto Space Sommandar, etc.), battle game War Riders, VR battle game Guild of Guardians. On April 1, Opensea also announced to integrate with Immutable X. Most of the NFT projects using Immutable X as the L2 scaling solution are games, of which Gods Unchained is the most well-known and representative one.
4.1.4 Feature Project: Gods Unchained
Gods Unchained is Immutable’s first blockchain-based e-sports game. It is a card trading game, similar to Hearthstone and the Elder Scrolls. Cards can be traded on Opensea and the card value varies based on the card rarity. Gods Unchained is one of the most popular NFT games. According to nongungible.com, its has exceeded US$20 million transaction value and 560,000 transaction volume as of now. In addition, according to nonfungible’s audit report published in January 2021, Whale’s vault owns 237 Gods Unchained NFT cards, 2% of the vault assets, and the cards are worth about US$240,000, 4% of the total vault asset value.
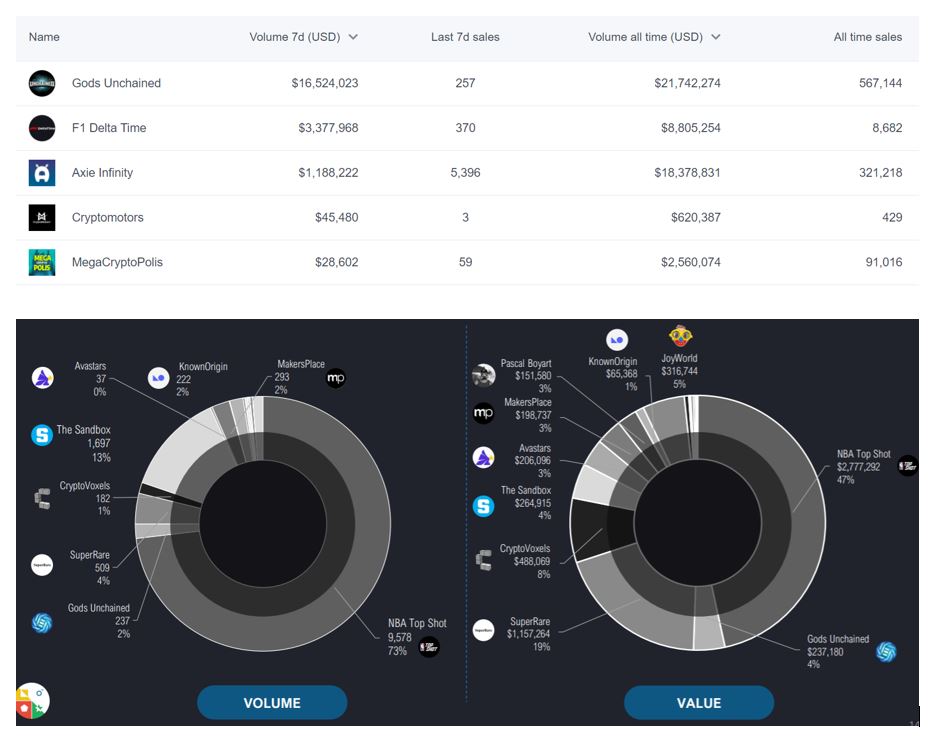
Figure 13. Portfolio Distribution of Whale Vault (source: nonfungible.com)
On March 22, Gods Unchained announced to connect with Immutable X as the L2 solution. It is the first Dapp to adopt Immutable X. Users can connect their wallets to Immutable X to enjoy low cost and fast transactions. On April 9, Immutable X stated that within 24 hours of the main net launch, Gods Unchained community saved over US$410,000 gas fee.
- Value of the Three Solutions
5.1 Pros and Cons
We do not think there will be an absolute winner among NFT infrastructure solutions including public blockchain, side chains and Layer 2 projects. Different applications will choose the suitable ones based on their own situations and requirements. The characteristics and applicable use cases of the three solutions are:
- Public blockchain: the advantage of public blockchain is that developers can work in the existing development environment without handling the cross-chain and antisynchronism issues between Ethereum main chains. However, it requires highly specialized nodes to handle the foundation-layer workload and decentralization might be compromised to some extent. In addition, there is no restriction on the applicable NFT use cases. But the public chain’s ecosystem and community activeness are the major considerations.
- Side chains: applying side chains to Dapps is fast and cheap, but security is the major concern. Compared to main chains, side chains are less strong in computing. It can be difficult to maintain the consensus mechanism and attacks may easily happen. Side chains are applicable to projects with small amount but high frequency transactions and willing to compromise some level of security, such as NFT trading platforms and games.
- Layer 2 Solutions: Layer 2, closely connected with the Ethereum main chain, can fully leverage Ethereum’s comprehensive financial infrastructure. Disadvantages differ among Layer 2 solutions (e.g. zk Rollup, Optimistic Rollup, etc.). They are more applicable to relatively mature Ethereum-based NFT projects which want to migrate a portion of functionalities or processes (e.g. migrating the voting function).
5.2 Outlook and Challenges
5.2.1 Leverage the token economy
For all kinds of infrastructure – new L1 public blockchain, side chains or L2 solutions – tokens can be used for governance, incentivizing nodes, maintaining and developing the community and ecosystem. This applies to both Defi and NFT. Particularly, ecosystems and communities are important for NFT projects. Tokens such as FLOW, NEAR and MATIC are effective in incentivizing participants. Governance tokens issued by infrastructure projects could be a potential investment direction.
5.2.2 Customized bottom-layer infrastructure becoming the standard
Based on Gods Unchained’s Immutable X and Axie Infinity’s Ronin, we believe that more and more projects will choose customized NFT infrastructure in the future, to meet their own customization requirements. Not limited to projects, IPs may also self-develop private infrastructure to launch their own NFT products and build the ecosystem. However, as the customized infrastructure matures and adds new functionalities, more applications will adopt it, making it no longer a private blockchain.
5.2.3 Emerging L1 and L2 integrated solutions
It is hard to find a balance among decentralization, security and scalability for scaling solutions. Some even believe it is a trilemma, which has been discussed in many articles about scaling solutions. We do not think there will be an absolute winner in NFT infrastructure. Instead, there will be more solutions integrating L1 and L2. For example, Polygon adopts Plasma and Rollup, as well as PoS side chains, in order to fulfil the needs of different developers.
5.2.4 Interoperability issue to be addressed
As mentioned earlier, L1 and L2 integrated solutions will be a development trend. Dapps may also deploy different functionalities to different solutions in the future. Interoperability solution is, therefore, a key area of development. Taking Opensea as an example, it integrates Flow, Polygon, and Immutable X. Different functions choose to migrate to different solutions. How a Dapp can interact between different solutions and how to provide a seamless user experience also need to be addressed in the future.
5.3 Technology, ecosystem, team and investors – key metrics of NFT infrastructure evaluation
5.3.1 Technical strength
Technical strength is the foundation for NFT infrastructure to survive in the market and the most important consideration factor when evaluating an early-stage infrastructure project. Whether the technology can be leveraged to solve the scalability issue and enhance user experience is the primary criteria when many NFT Dapps choose migration solutions. Leading solutions such as Flow, Near and Polygon have their proprietary technologies. Players can evaluate the technical strength of a network based on the project whitepaper and external media review.
5.3.2 Ecosystem completeness
Apart from technical strength, the ecosystem quality determines whether the infrastructure can be sustainable in the long run. Ethereum is an example. The number and quality of Dapps as well as access to IP resources are key metrics to evaluate the quality of a NFT infrastructure ecosystem.
- The number and quality of Dapps: The number of Dapps is easy to understand. Statistics websites such as DappRadar or project websites can be referenced to check the list of NFT Dapps on a blockchain network. In terms of quality, key indicators include active user base, transaction volume, community activeness, and external review. Assessing the number and quality of NFT Dapps is valuable to determine whether that network is suitable to build NFT projects.
- Access to IP resources: A key difference between NFT and Defi is that NFT represents the tokenization of more real-life hobbies and has higher requirements on entertainment, social engagement and markets. High-quality IPs usually bring significant attention to the projects, driving the integration of capital and market adoption and ensuring a sufficient audience base. Access to IP resources is particularly critical in the competition of NFT public blockchains. Flow is a reference of good access to IP resources.
5.3.3 Team background and Investors
Users can assess whether the NFT infrastructure development team has built any successful similar projects previously. The familiarity of team members on NFT could be a supporting metric. Examples are Crypto Kitties by Dapp Labs and Gods Unchained by Immutable. In addition, investments by large institutional investors are also valuable references, such as a16z, Coinbase Ventures, DCG, USV, Coin Fund, Venrock, etc.



